Introduction
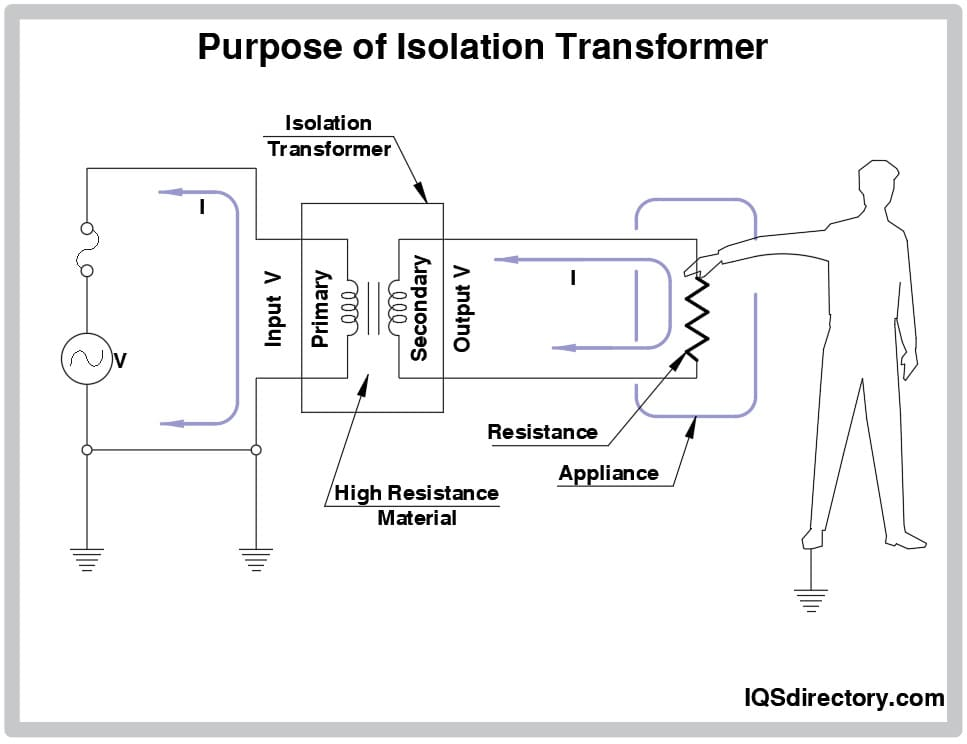
Isolation transformers play a crucial role in electrical systems by providing galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. They help in preventing ground loops, suppressing electrical noise, and ensuring safe power transmission. These transformers are widely used in industrial automation, medical equipment, data centers, and sensitive electronic devices.
Choosing the right isolation transformer requires a deep understanding of its types, features, and applications. Selecting a transformer from a reliable isolation transformers manufacturer ensures optimal performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. The design, voltage rating, insulation, and cooling mechanism all contribute to the overall efficiency of an isolation transformer.
This guide provides detailed insights into isolation transformer selection, including technical specifications, pricing considerations, and industry applications.
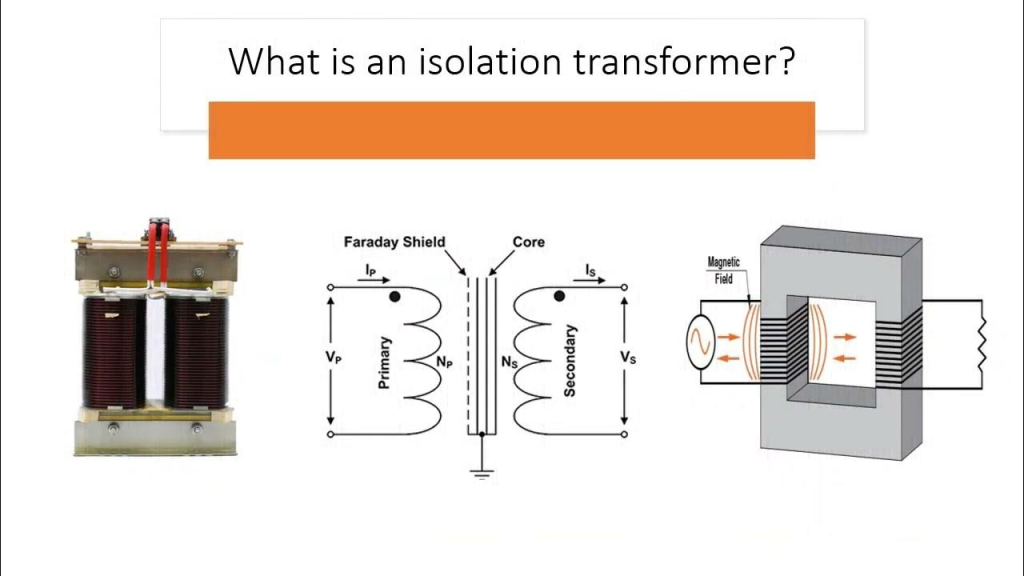
What is an Isolation Transformer?
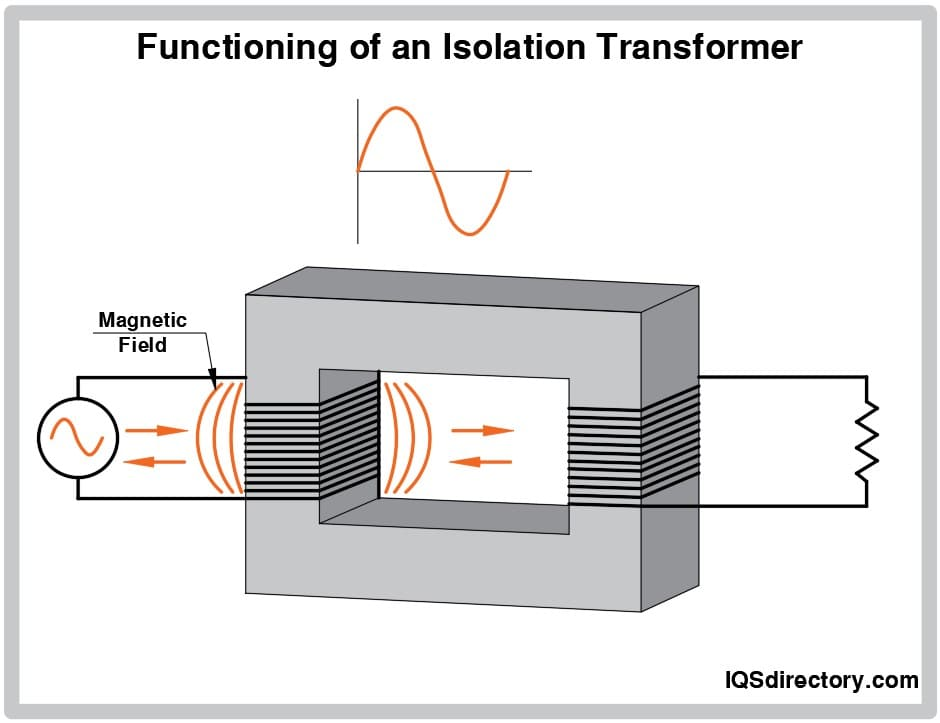
An isolation transformer is a type of transformer that electrically separates the input and output circuits while allowing power transfer through electromagnetic induction. Unlike conventional transformers, it does not have a direct conductive path between the primary and secondary windings.
Key Functions of Isolation Transformers
- Electrical Safety: Prevents electric shock by isolating the load from the main power supply.
- Noise Reduction: Eliminates common-mode noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Voltage Regulation: Ensures stable power supply for sensitive electronic devices.
- Ground Loop Prevention: Reduces the risk of unwanted current flow between interconnected devices.
- Surge Protection: Shields connected equipment from power surges and transients.
These advantages make isolation transformers essential in industries where power quality and equipment protection are critical.
Types of Isolation Transformers
Choosing the right type of isolation transformer depends on the application and power requirements. Here are the most common types:
1. Single-Phase Isolation Transformers
- Used for low-power applications such as home appliances, medical devices, and office equipment.
- Typically available in voltage ratings of 120V, 240V, and 480V.
- Compact and energy-efficient for localized power isolation.
2. Three-Phase Isolation Transformers
- Designed for industrial applications requiring high-power loads.
- Commonly used in data centers, manufacturing plants, and large machinery.
- Provides balanced voltage distribution and minimizes power fluctuations.
3. Medical-Grade Isolation Transformers
- Used in hospitals and laboratories to ensure patient safety.
- Equipped with ultra-low leakage current to prevent electrical hazards.
- Ensures clean power supply for critical medical equipment such as MRI machines, X-ray devices, and surgical instruments.
4. K-Rated Isolation Transformers
- Designed for environments with high harmonic distortion.
- Used in data centers, telecom networks, and industrial automation systems.
- Prevents overheating and extends equipment lifespan.
5. Auto Isolation Transformers
- Features a single winding with tapped connections for different voltage outputs.
- More compact and cost-effective but offers limited isolation compared to standard transformers.
- Commonly used in small-scale electronic systems and automation.
Selecting the right type depends on the load, operating environment, and safety requirements.
Features to Consider When Selecting an Isolation Transformer
1. Voltage and Power Rating
- Ensure that the transformer’s primary and secondary voltage ratings match your application.
- Power capacity should be sufficient to handle the connected load without overheating.
2. Efficiency and Energy Losses
- High-efficiency transformers minimize energy losses and improve overall system performance.
- Copper and core losses should be evaluated to reduce unnecessary power consumption.
3. Cooling Mechanism
- Air-Cooled (Dry-Type): Suitable for indoor applications with moderate power loads.
- Oil-Cooled: Used in high-power applications requiring superior heat dissipation.
4. Insulation and Dielectric Strength
- High insulation resistance ensures better protection against electrical faults.
- Dielectric strength indicates the transformer’s ability to withstand voltage surges.
5. EMI and Noise Suppression
- Shielded isolation transformers are recommended for reducing electromagnetic interference.
- Essential in laboratories, audio processing systems, and communication networks.
6. Compliance with Standards
- Look for transformers that meet industry certifications such as UL, CE, ISO, and IEC.
- Compliance ensures reliability and adherence to safety regulations.
Choosing an isolation transformer with these features guarantees optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Considerations: Understanding Isolation Transformer Price
The isolation transformer price varies based on several factors, including:
1. Transformer Type and Power Rating
- Single-phase transformers are generally more affordable than three-phase models.
- Higher power ratings increase the overall cost due to material and design complexity.
2. Core Material and Build Quality
- Silicon Steel Cores: Common and cost-effective for general applications.
- Amorphous Cores: Higher efficiency but more expensive.
3. Cooling Method
- Dry-Type Isolation Transformers: Lower initial cost, suitable for indoor environments.
- Oil-Cooled Isolation Transformers: Higher upfront cost but better suited for heavy-duty industrial applications.
4. Customization and Additional Features
- Custom-built transformers with specific shielding, insulation, and surge protection cost more.
- Medical-grade and industrial-grade transformers have premium pricing due to enhanced safety features.
5. Brand and Manufacturer Reputation
- Well-known isolation transformers manufacturers charge a premium for reliability and warranty coverage.
- Generic or low-quality transformers may be cheaper but can compromise performance and safety.
When evaluating isolation transformer prices, consider long-term efficiency and durability to ensure value for investment.
Applications of Isolation Transformers
1. Medical and Healthcare Industry
- Used in MRI machines, CT scanners, and surgical equipment to prevent electrical shock.
- Ensures stable and noise-free power supply for life-saving devices.
2. Data Centers and IT Infrastructure
- Protects servers, routers, and storage systems from voltage fluctuations.
- Reduces downtime and prevents data corruption due to power instability.
3. Industrial Automation
- Used in CNC machines, robotics, and process control systems for consistent voltage supply.
- Prevents ground loops in complex industrial networks.
4. Telecommunications
- Ensures reliable power for switching systems, transmission towers, and network equipment.
- Shields sensitive communication devices from electromagnetic interference.
5. Renewable Energy Systems
- Used in solar and wind power installations to isolate grid connections.
- Prevents back-feeding issues and ensures stable voltage output.
Isolation transformers are indispensable across multiple industries for enhancing power quality and equipment protection.

Conclusion: Selecting the Right Isolation Transformer 240V Model
Choosing the best isolation transformer depends on application requirements, efficiency, and cost considerations. For general-purpose applications, an isolation transformer 240V is a popular choice, commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial setups. It ensures safe voltage regulation, electrical isolation, and protection against power surges.
For businesses and industries requiring reliable isolation transformers, selecting a reputable isolation transformers manufacturer guarantees high-quality performance, compliance with safety standards, and long-term durability. Before making a purchase, evaluating isolation transformer price, load capacity, and environmental factors helps in choosing the best model for specific needs.
Power quality is crucial for operational efficiency, isolation transformers serve as a vital component in electrical networks. By preventing electrical faults, reducing noise interference, and ensuring stable power distribution, these transformers contribute significantly to the safety and reliability of electrical systems worldwide.

