Electricity plays a vital role in powering industries, businesses, and residential areas across the globe. However, the voltage required at the generation point often differs from what’s needed at the consumption point. That’s where transformers—especially step up transformer units—become essential components in the power distribution process.
A step-up transformer increases the voltage from a lower level to a higher level, making it suitable for long-distance transmission and specific industrial applications. This article examines the advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications of step-up transformers in various fields, including their differences from their counterpart, the step-down transformer.
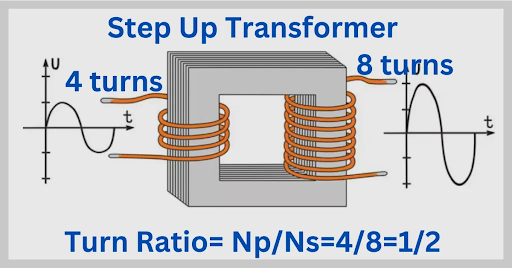
Step-up vs Step-down Transformers: What’s the Difference?
Transformers are of two main types—step-up and step-down. The difference lies in the direction of voltage transformation.
- A step-up transformer converts low-voltage, high-current input to high-voltage, low-current output.
- A step-down transformer, on the other hand, converts high-voltage input to a lower voltage suitable for use in homes, labs, or specific machines.
If you’re looking for a step down transformer in Chennai, it’s likely for commercial or residential equipment that operates on lower voltage standards.
Understanding this distinction is key when choosing the right transformer for your specific application.
Need a Step-Down Transformer For Your Manufacturing Company?
Get Quote Now!
Can You Use a Step-down Transformer Instead?
This is a common question in many industrial and commercial setups. Some users mistakenly think that one type of transformer can be used interchangeably. However, transformers must match the voltage needs of your equipment and installation.
For instance, if your imported equipment requires 110V but your mains supply is 230V, you’ll need to buy step down transformer to safely power the equipment. Similarly, if your machinery needs a boost in voltage for efficient operation or grid connection, a step-up transformer is the answer.
How Does a Step-up Transformer Work?
A step-up transformer has:
- More turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil
- This design increases the voltage on the output side while proportionally decreasing the current
The principle is based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, which states that a change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
Use Case Example:
If you input 230V on the primary side and your secondary coil has twice the number of turns, your output voltage would be approximately 460V—ideal for transmission or powering high-voltage machines.
Advantages of Step-up Transformers
Here’s a detailed look at why step-up transformers are widely used across industries:
1. Efficient Long-Distance Transmission
High-voltage transmission reduces power loss due to resistance in the wires. Since power loss = I²R, lowering the current (by increasing the voltage) significantly minimizes energy dissipation over long distances.
Use Case: Power generation plants use step-up transformers to transmit electricity to substations hundreds of kilometers away.
2. Supports Heavy Industrial Loads
Industries that operate heavy-duty machinery—like CNC machines, compressors, or large motors—often require higher voltages. A step-up transformer ensures that machines get the exact voltage needed for optimal performance.
Industries Benefiting:
- Oil & Gas
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Mining
- Chemical Processing
3. Ideal for Renewable Energy Systems
Solar and wind energy systems generate DC power at lower voltages, which needs to be stepped up before feeding into the power grid. Step-up transformers play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy into national grids.
4. Voltage Matching for Imported Equipment
Some imported machines or equipment (especially from the US or Japan) require higher voltages than what’s standard in India. A step-up transformer ensures compatibility and safe operation.
5. Consistent and Stable Output
Step-up transformers provide regulated voltage levels to connected equipment, ensuring consistent output and protection against under-voltage damage.
6. Low Maintenance and High Durability
These transformers are built to last. Once installed, they require minimal maintenance and can function efficiently for years without breakdowns, especially when sourced from quality manufacturers.
7. No Moving Parts
As they operate based on electromagnetic principles, step-up transformers don’t have moving parts, reducing mechanical wear and extending equipment life.
8. Wide Application Versatility
Step-up transformers are used in:
- Power plants
- Substations
- Research labs
- Aerospace systems
- Renewable energy farms
- Industrial motors
Need a Step-Down Transformer For Your Manufacturing Company?
Get Quote Now!
Disadvantages of Step-up Transformers
Despite their many benefits, step-up transformers are not without limitations. Let’s explore their drawbacks:
1. Higher Output Voltage Can Be Hazardous
The elevated voltage output must be handled with extreme care. Improper installation or lack of protective equipment can lead to serious accidents or equipment damage.
Solution: Always include fuses, MCBs, and surge protection systems in the setup.
2. Size and Weight
Step-up transformers with large capacities can be bulky and require dedicated space for installation. This may not be feasible for compact environments.
3. Initial Cost Can Be High
High-capacity industrial-grade step-up transformers can be expensive upfront. However, the ROI (Return on Investment) is justifiable through energy savings and equipment protection over time.
4. Requires Professional Installation
Installing or configuring a step-up transformer incorrectly can lead to serious failures. You must rely on certified electricians or manufacturer-backed teams for installation and testing.
5. Limited Flexibility
A transformer is built for a specific voltage ratio. If your system needs change (e.g., switching to lower-voltage machinery), the same transformer may become unusable.
🏭 Where Are Step-up Transformers Commonly Used?
Here’s a sector-wise breakdown of applications:
Sector | Use Case |
Power Generation | Transmit power to substations at high voltage |
Renewable Energy | Boost voltage from solar/wind sources for grid input |
Oil & Gas | High-voltage equipment and drilling operations |
Research & Labs | Specialized instruments requiring stable high voltage |
Aerospace | Satellite launch equipment and control stations |
Railways | Powering electric locomotives and control centers |
Key Specs to Consider When Buying a Step-up Transformer
When selecting a transformer for your facility or project, consider:
- Input & Output Voltage Ratings
- Power Capacity (in kVA or kW)
- Phase Type (Single or Three Phase)
- Cooling Type (Air-cooled or Oil-cooled)
- Winding Material (Copper or Aluminum)
- Insulation Class
- Certifications (IS, CE, ISO)
Professional guidance from trusted electrical equipment providers will help you get the right configuration tailored to your load profile.
Real-World Case Example
A textile mill in Tamil Nadu installed a step-up transformer to boost voltage from 415V to 660V to power their German-imported spinning machinery. This allowed them to:
- Increase machine efficiency by 15%
- Reduce start-up load failures
- Lower electricity costs through efficient operation
With proper installation and load management, their transformer has been running for 6+ years with only minor maintenance.
Safety Tips When Using a Step-up Transformer
- Always install protective relays and fuses
- Ensure proper earthing of the transformer body
- Use surge protection devices (SPD)
- Keep the area dry and well-ventilated
- Don’t exceed the rated capacity under any circumstances
- Perform insulation resistance testing during yearly maintenance
- Ensure input and output cables are correctly rated for current draw
Step-up Transformer vs Servo Stabilizer: When to Use What?
Feature | Step-up Transformer | Servo Stabilizer |
Primary Purpose | Increase voltage | Regulate fluctuating voltage |
Voltage Adjustment | Fixed ratio (e.g., 230V to 460V) | Dynamic, real-time voltage correction |
Output Accuracy | Limited (no correction during fluctuation) | ±1% precise output |
Use Case | Voltage boosting | Voltage regulation & equipment protection |
In most industrial setups, both devices may work together—a step-up transformer to raise voltage, and a servo stabilizer to ensure that voltage stays stable.
Conclusion
A step-up transformer is a powerful asset when used correctly. From power plants and renewable energy farms to advanced industrial machinery, step-up transformers enable high-voltage operation, long-distance power transmission, and equipment compatibility.
While they offer many advantages like energy efficiency, durability, and wide applications, it’s important to be mindful of safety, proper sizing, and certified installation. For industries in and around Tamil Nadu, working with reputed servo stabilizer manufacturers in Chennai or transformer suppliers ensures high-quality, ISI-certified, and application-matched solutions.
The right transformer doesn’t just deliver power—it delivers performance, protection, and peace of mind.

